One of the first requirements for the flight crew on initialising the avionics is to check if the Navigation Database is current and up-to-date. This will be indicated by the active AIRAC cycle dates. Flight crews should not operate with an out-of-date Navigation Database as the information being used by the computer may not be current.
However, there may be times when an out-of-date database may be used and these exceptions should be clearly defined within the MEL.
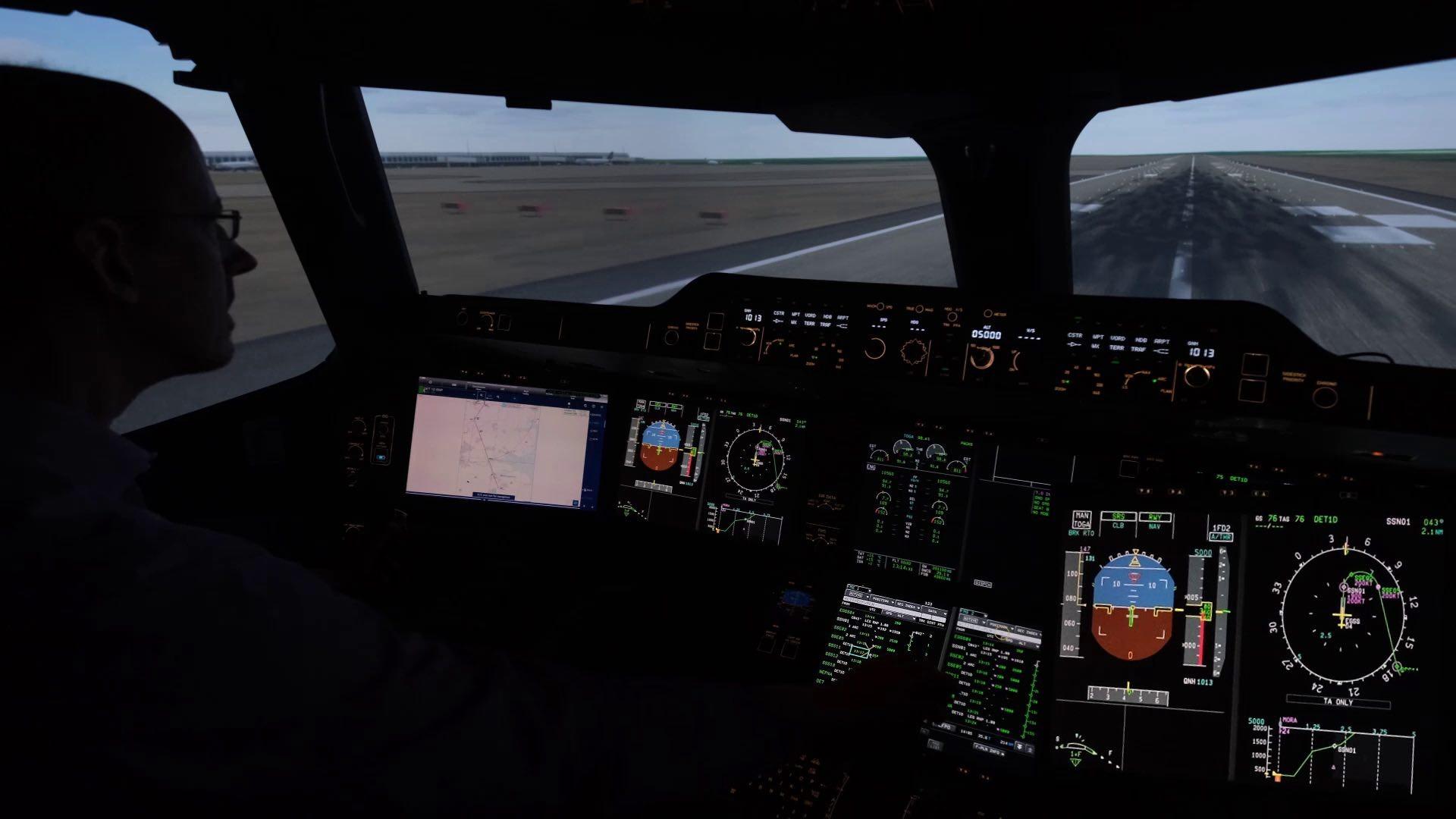
Change of departure clearance during taxi (Brussels, Belgium)
The video, recorded in an Airbus A319, demonstrates the tasks a flight crew needs to perform during the taxi phase before departure. Normally the departure clearance is received before engine start-up. When ATC issues a revised departure route during taxi, the flight crew needs to reprogram the FMS and brief the new route, which causes extra workload in the cockpit.
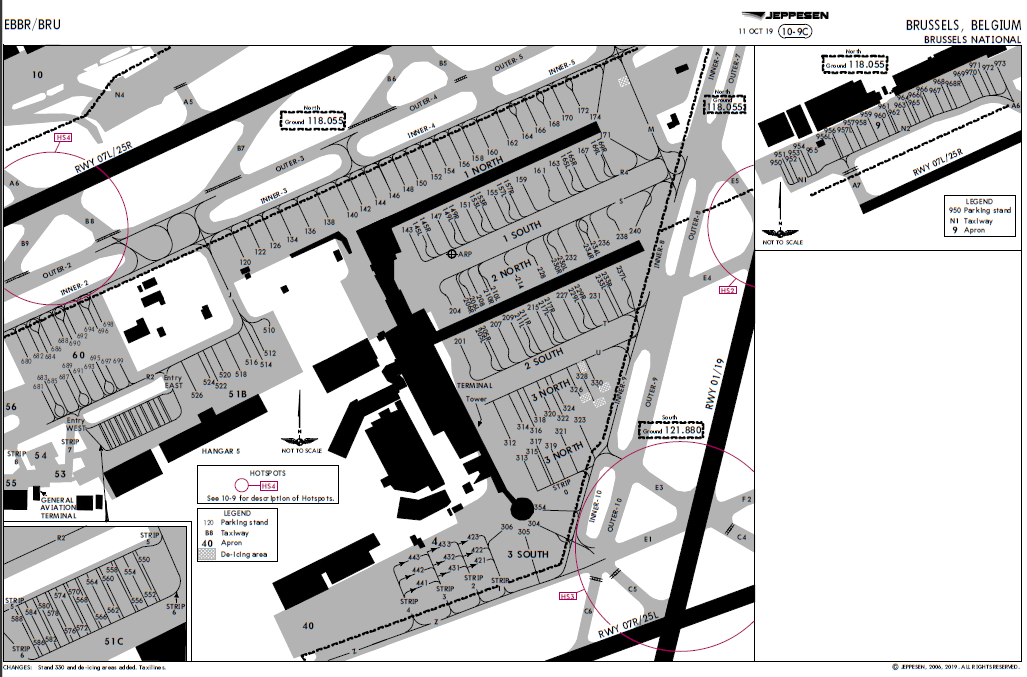
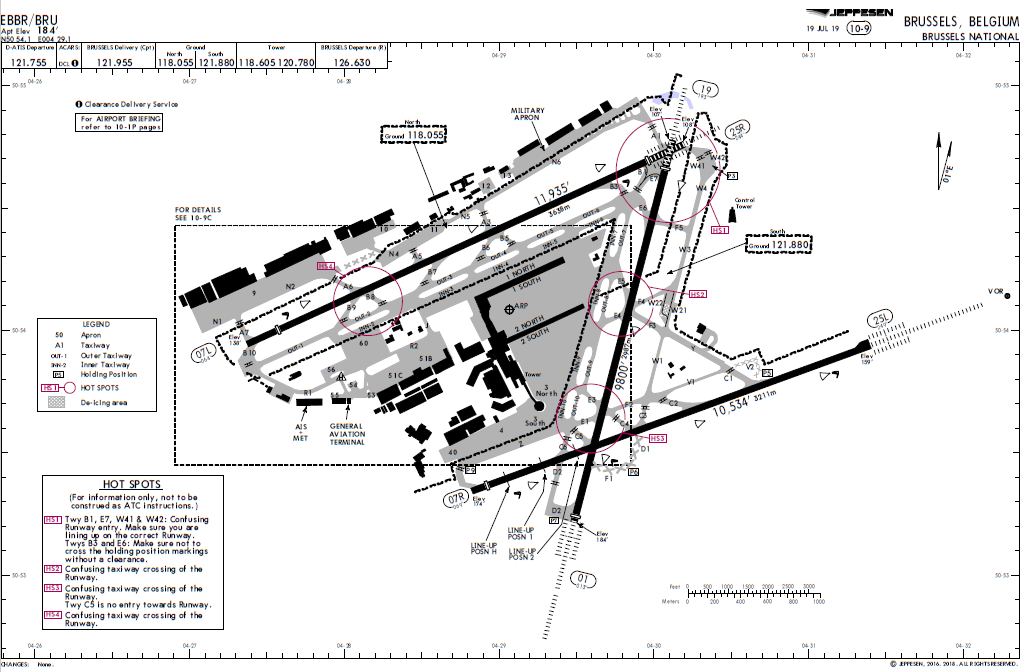
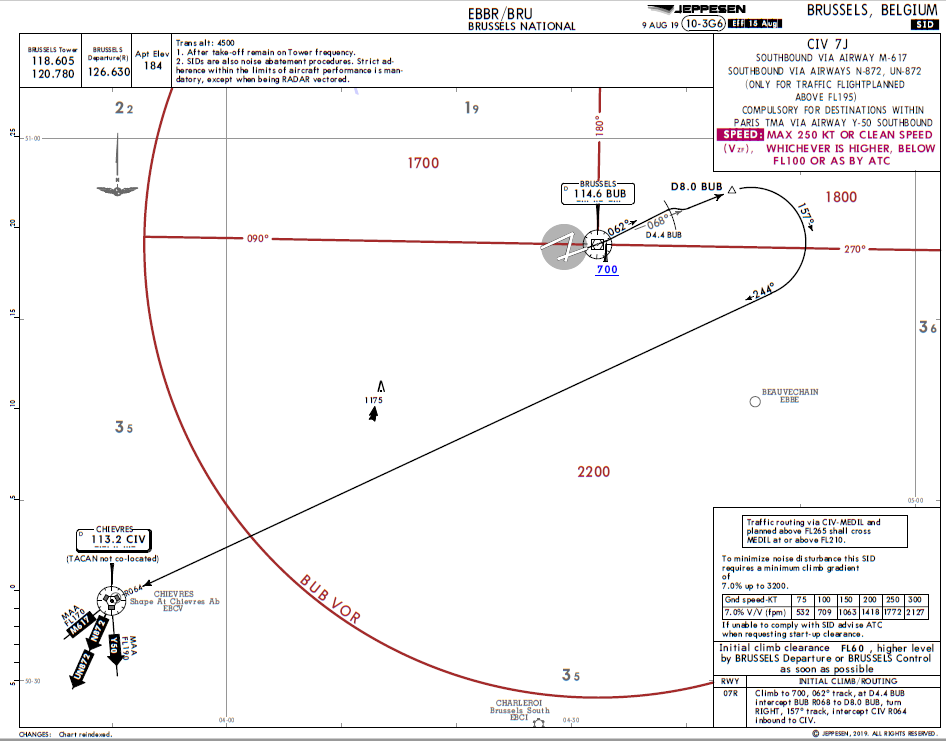
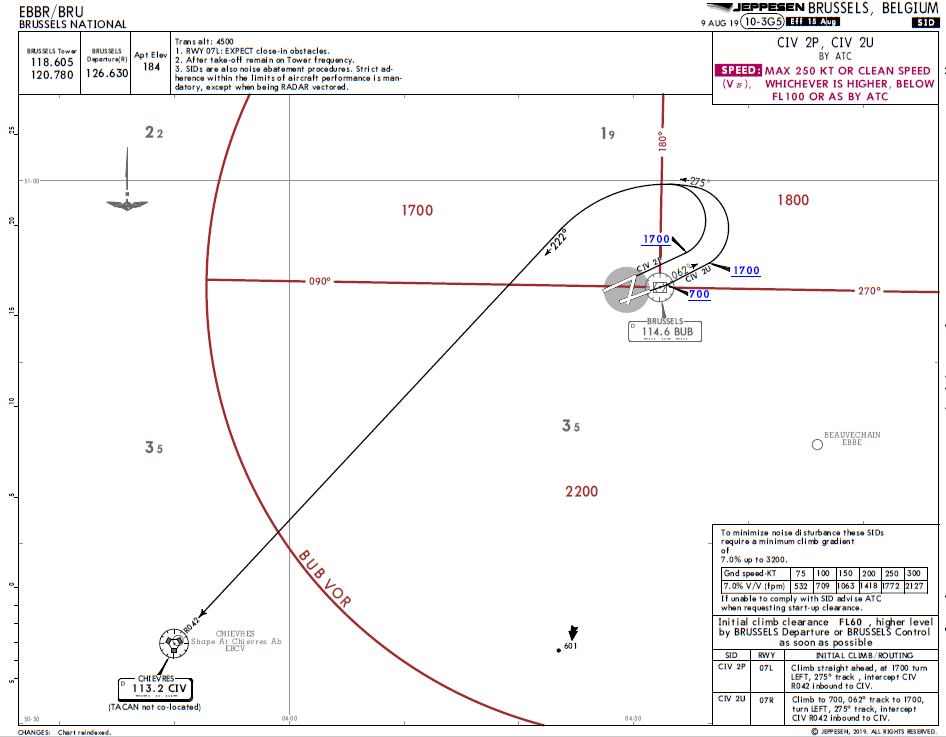
Brussels (EBBR) Charts - Select icons below to open
Continuous Climb Operations (CCO) is an aircraft operating technique enabled by airspace design, instrument flight procedure design and facilitated by air traffic control (ATC). CCO allow aircraft to follow an optimum flight path that delivers major environmental and economic benefits - reduced fuel burn, gaseous emissions, noise and fuel costs - without any adverse effect on safety.
CCO operations allow departing aircraft to climb continuously, to the greatest extent possible. Aircraft applying CCO employ optimum climb engine thrust and climb speeds until reaching their cruising levels. Employment of this technique reduces intermediate level-offs and results in time being spent at more fuel-efficient higher cruising levels, hence significantly reducing fuel burn and lowering emissions and fuel costs.
Click here for more information on CCO.
